



Next: [Allen et al. (1995)]
Up: No Title
Previous: ZND Calculation Results
Reaction Mechanisms
The core of chemical kinetics calculations is the reaction mechanism,
which specifies the set of elementary reactions to be considered and
the rate parameters that describe the temperature dependency of the
rates of these reactions. The rate equation used is the modified
Arrhenius equation, which requires three parameters:
The dimensions of k are
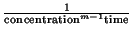 where m is the order of the reaction. The temperature exponent n is
dimensionless while temperature is understood to be in K. The activation
energy E has dimensions of energy/mole, although sometimes the ratio
E/R is provided instead, which has a dimension of temperature.
In the tables of reaction mechanisms below, units have not been used
consistently so the units of each table are provided in the header.
Most elementary reactions described below are bidirectional, meaning that
the rate parameters for one direction are provided, but the reverse rates
can be computed through equilibrium considerations. Some reactions are
specified as unidirectional (by
where m is the order of the reaction. The temperature exponent n is
dimensionless while temperature is understood to be in K. The activation
energy E has dimensions of energy/mole, although sometimes the ratio
E/R is provided instead, which has a dimension of temperature.
In the tables of reaction mechanisms below, units have not been used
consistently so the units of each table are provided in the header.
Most elementary reactions described below are bidirectional, meaning that
the rate parameters for one direction are provided, but the reverse rates
can be computed through equilibrium considerations. Some reactions are
specified as unidirectional (by
 ), generally because rate
data are directly available for the reverse reaction. Other annotations
are consistent with conventions of the Sandia gas phase chemical kinetics
package [Kee
et al. (1989)]. In
calculations performed with these mechanisms for this report, thermodynamic
data were obtained from the Sandia thermodynamic database whenever possible.
Where data were not available from this database, they were taken from the
GRI thermodynamic database [Frenklach et al. (1995)].
), generally because rate
data are directly available for the reverse reaction. Other annotations
are consistent with conventions of the Sandia gas phase chemical kinetics
package [Kee
et al. (1989)]. In
calculations performed with these mechanisms for this report, thermodynamic
data were obtained from the Sandia thermodynamic database whenever possible.
Where data were not available from this database, they were taken from the
GRI thermodynamic database [Frenklach et al. (1995)].




Next: [Allen et al. (1995)]
Up: No Title
Previous: ZND Calculation Results
Joe E. Shepherd
2000-01-17